logP Plugin
This manual gives you a walk-through on how to use the logP Plugin:
Introduction
The logP Plugin calculates the octanol/water partition coefficient, which is used in QSAR analysis and rational drug design as a measure of molecular hydrophobicity. The calculation method is based on the publication of Viswanadhan et al. The logP of a molecule is composed of the increment of its atoms. However, the algorithm described in the paper was modified at several points:
-
Many atomic types were redefined to accommodate electron delocalization and contributions of ionic forms were added.
-
The logP of zwitterions are calculated from their logD value at their isoelectric point.
-
The effect of hydrogen bonds on the logP is considered if there is a chance to form a six membered ring between suitable donor and acceptor atoms.
-
New atom types were introduced especially for sulfur, carbon, nitrogen and metal atoms.
To find details on logP calculation, see the following page.
The result of the calculation appears in a new window, either in a MarvinView (for a 2D view) window or in a MarvinSpace (for a 3D view) window.
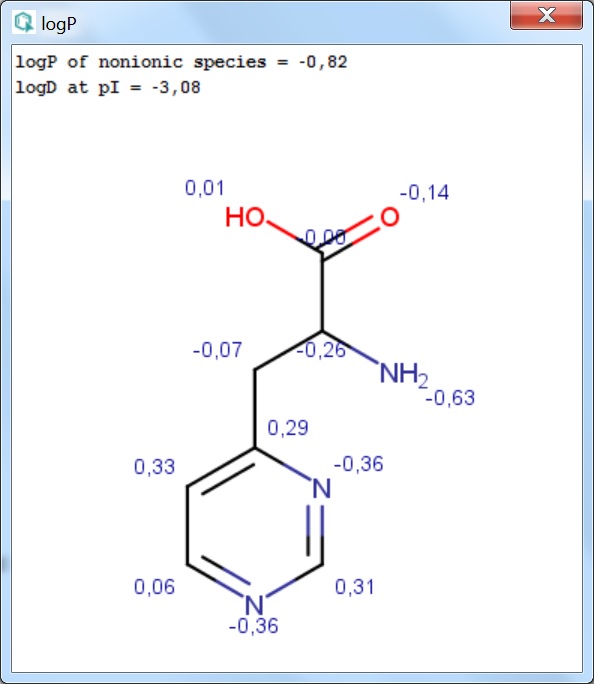
Fig. 1 LogP result window with atomic increments displayed in MarvinView
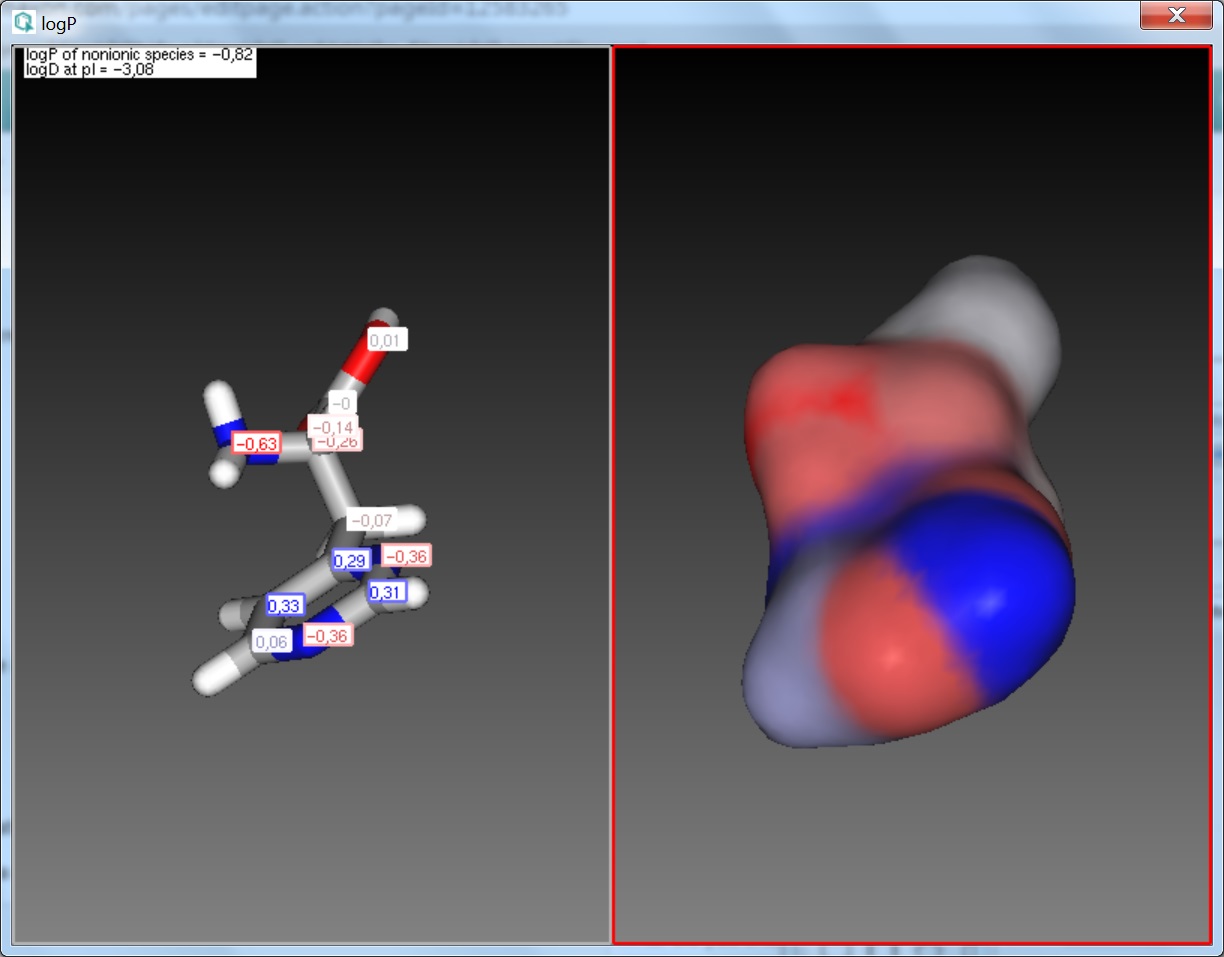
Fig. 2 LogP result window with atomic increments displayed in MarvinSpace
Options
General Options
Different general options can be set in the logP Options window:
Method
This option defines the method for calculating logP. These can be:
-
Consensus: this method uses a consensus model built on the ChemAxon and Klopman et al. models and the PhysProp database.
-
ChemAxon: this method is based on ChemAxon's own logP model, which is based on the VG method (derived from Viswanadhan et al.). Read more about it here.
-
User defined: if a training set of structures and corresponding experimental logP values is available, it can be used as a database for logP calculations. See the manual page on creating such training sets.
Other options
These options are for refining the logP calculation.
-
Training ID: if the User defined method is selected, this dropdown list becomes active. All created training sets are listed here. Choose the one to apply for the calculation.
-
Electrolyte concentration
-
Cl- concentration: can be set between 0.1 and 0.25 mol/L.
-
Na+ K+ concentration: can be set between 0.1 and 0.25 mol/L.
-
-
Consider tautomerization/resonance: the logP of the major tautomer will be calcutated if enabled.
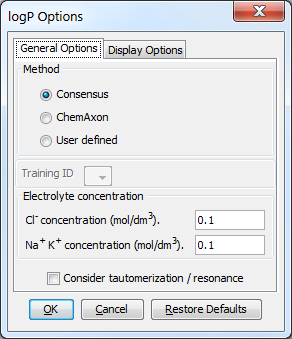
Fig. 3 logP Options window with the General Options panel
Display Options
Different display options can be set in the logP Options window:
-
Decimal places: setting the number of decimal places for the precision of the result value.
-
Show value: sets which logP values be displayed in the result window. It can be:
-
Increments: calculates and shows the increments for atoms one-by-one.
-
logP : shows just the value of the logP.
-
-
Display in MarvinSpace: the result window opens as 3D MarvinSpace viewer. If unchecked, the results will be shown in a 2D MarvinView panel.
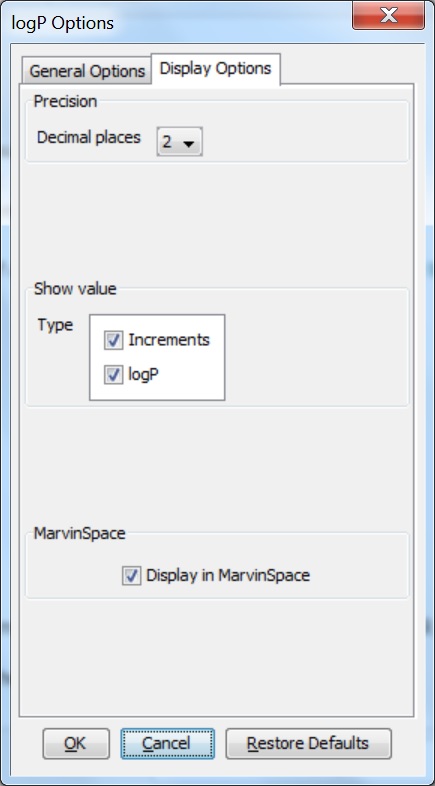
Fig. 4 logP Options window with the Display Options panel
References
-
Viswanadhan, V. N.; Ghose, A. K.; Revankar, G. R.; Robins, R. K., J. Chem. Inf. Comput. Sci., 1989, 29, 163-172; doi
-
Klopman, G.; Li, Ju-Yun.; Wang, S.; Dimayuga, M.: J.Chem.Inf.Comput.Sci., 1994, 34, 752; doi
-
PHYSPROP© database
-
Csizmadia, F; Tsantili-Kakoulidou, A.; Pander, I.; Darvas, F., J. Pharm. Sci., 1997, 86, 865-871; doi