Differences between the Basic and General methods
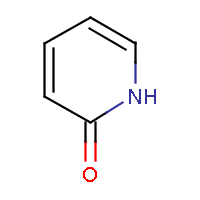
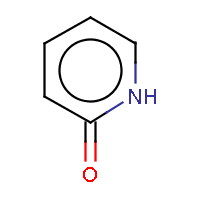
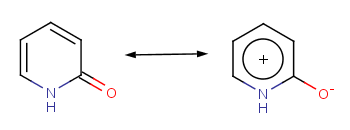
The two method approach the question differently. The general method tries to incorporate mesomeric, tautomeric rearrangement, as in 2-pyridone, while the basic method does not. In the basic method the external double bond breaks the formation of aromatic ring.
The 2-pirydone is aromatic due to its mesomeric rearrangement:
The following molecules will give different results depending upon the method applied.
|
Molecule in aliphatic form |
Basic aromatization |
General aromatization |
|
IUPAC name: pyridin-2(1H)-one |
||
|
|
|
|
|
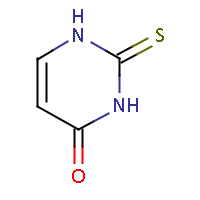
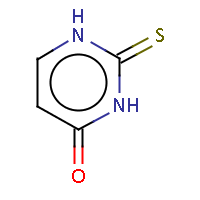
IUPAC name: 2-thioxo-2,3-dihydropyrimidin-4(1H)-one |
||
|
|
|
|
|
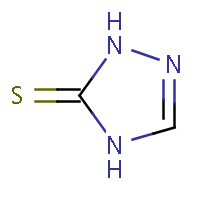
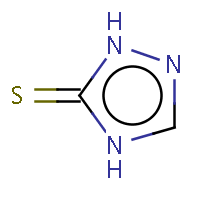
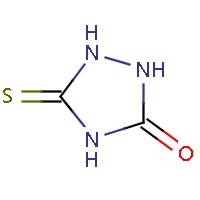
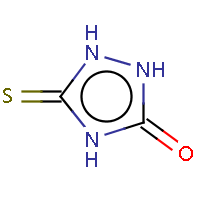
IUPAC name: 2,4-dihydro-3H-1,2,4-triazol-3-thione |
||
|
|
|
|
|
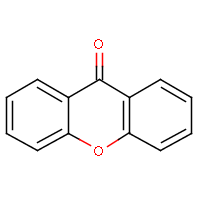
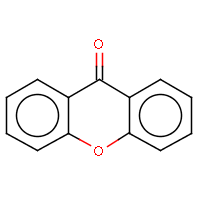
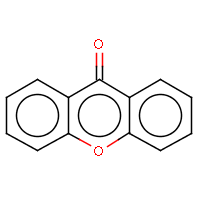
IUPAC name: 9H-xanthen-9-one |
||
|
|
|
|
|
IUPAC name: 5-thioxo-1,2,4-triazolidin-3-one |
||
|
|
|
|
|
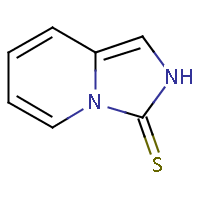
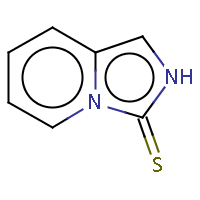
IUPAC name: imidazo[1,5-a]pyridine-3(2H)-thione |
||
|
|
|
|