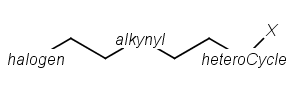
Homology Groups
Homology groups stand for sets of homologous molecular parts (e.g. functional groups). These are represented by pseudo atoms labelled with the common chemical annotation of the groups (alkyl, aryl, heterocycle etc.).
See the detailed definition of these groups in a separate document. The pseudo atoms can be most easily drawn in Marvin Sketch using the Homology Groups template group.
|
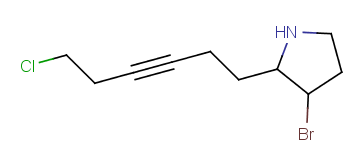
Example |
Example Markush library member |
|
|
|
There are two major types of homology groups regarding their way of definition:
-
Built-in groups are defined by specific structural properties of the group. These groups are not enumerated during searching, but the query structure is recognized as fulfilling the requirements for such a structure. The possible number of covered structures is usually infinite, unless the number of atoms is limited. Examples of built-in groups are alkyl, aryl, heterocycle, etc.
-
User-defined groups are explicitly defined and only the listed structures can match on these homology groups. The definition is given in the form of an R-group definition, and any of the generic features discussed in this chapter can be used in the definition. These definitions can be customized by the user, and may be context-specific. (E.g. protecting group definition depends on which functional group it is protecting.)
Read more about homology groups.