Topological Analysis Plugin
This manual gives you a walk-through on how to use the Topological Analysis Plugin:
Introduction
The Topology Analysis Plugin calculates different topological descriptors for a molecule. The example below shows the result window of the plugin.
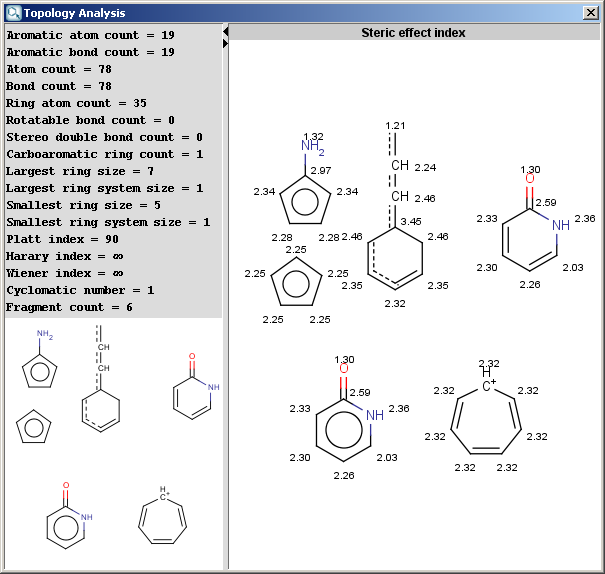
Fig.1 Topological descriptors calculated and displayed for molecules
These options can be set in the Topology Analysis Options window, as shown below with the Atom/Bond Tab opened.
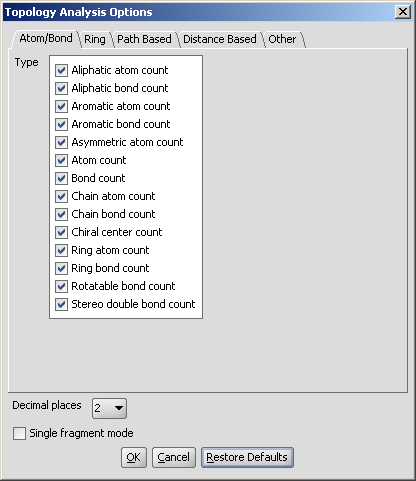
Fig. 2 Topology Analysis Options window
The Decimal places and the Single fragment mode set the number of decimal places for the calculation results and the displaying mode of the molecules, respectively.
Available topological descriptors
The following descriptors can be calculated (each group of descriptors can be found under a separate tab of the options window):
Atom/bond descriptors
-
Aliphatic atom count: number of atoms in the molecule having no aromatic bond (excluding hydrogens).
-
Aliphatic bond count: number of non-aromatic bonds in the molecule (excluding bonds of hydrogen atoms).
-
Aromatic atom count: number of atoms in the molecule having aromatic bonds.
-
Aromatic bond count: number of aromatic bonds in the molecule.
-
Asymmetric atom count: the number of asymmetric atoms (having four different ligands).
-
Atom count: number of atoms in the molecule including hydrogens.
-
Bond count: number of bonds in the molecule including bonds of hydrogen atoms.
-
Chain atom count: number of chain atoms (non-ring atoms excluding hydrogens).
-
Chain bond count: number of chain bonds (non-ring bonds excluding bonds of hydrogen atoms).
-
Chiral center count: the number of tetrahedral stereogenic centers. This function identifies two chiral centers in 1,4-dimethylcyclohexane, which does not contain asymmetric atoms.
-
Ring atom count: number of ring atoms.
-
Ring bond count: number of ring bonds.
-
Rotatable bond count: number of rotatable bonds in the molecule. Unsaturated bonds, and single bonds connected to hydrogens or terminal atoms, single bonds of amides, sulphonamides and those connecting two hindered aromatic rings (having at least three ortho substituents) are considered non-rotatable.
-
Stereo double bond count: number of double bonds with defined stereochemistry.
Ring descriptors
-
Aliphatic ring count: number of those rings in the molecule that have non-aromatic bonds (SSSR based).
-
Aromatic ring count: number of aromatic rings in the molecule. This number is calculated from the smallest set of smallest aromatic rings (SSSAR), which might contain rings which are not part of the standard SSSR ring set. As a consequence, the sum of the aliphatic ring count and the aromatic ring count can sometimes be greater than the ring count value. The difference is the signal of a macroaromatic ring system.
-
Carbo ring count: number of rings containing only carbon atoms.
-
Carboaliphatic ring count: number of aliphatic rings containing only carbon atoms.
-
Carbooaromatic ring count: number of aromatic rings containing only carbon atoms (SSSAR based).
-
Fused aliphatic ring count: number of aliphatic rings having common bonds with other rings.
-
Fused aromatic ring count: number of aromatic rings having common bonds with other rings.
-
Fused ring count: number of fused rings in the molecule (having common bonds).
-
Hetero ring count: number of rings containing hetero atom(s).
-
Heteroaromatic ring count: number of aromatic heterocycles in the molecule.
-
Largest ring size: size of the largest ring in the molecule.
-
Largest ring system size: number of rings in the largest ring system.
-
Ring count: number of rings in the molecule. This calculation is based on SSSR (Smallest Set of Smallest Rings).
-
Ring system count: number of disjunct ring systems.
-
Smallest ring size: size of the smallest ring in the molecule.
-
Smallest ring system size: number of rings in the smallest ring system.
Path-based descriptors
-
Platt index: sum of the edge degrees of a molecular graph.
-
Randic index: harmonic sum of the geometric means of the node degrees for each edge.
Distance-based descriptors
-
Balaban index: the Balaban distance connectivity of the molecule, which is the average distance sum connectivity.
-
Distance degree: the sum of the corresponding row values in the distance matrix for each atom.
-
Eccentricity: the greatest value in the corresponding row of the distance matrix for each atom.
-
Harary index: half-sum of the off-diagonal elements of the reciprocal molecular distance matrix of the molecule.
-
Hyper Wiener index: a variant of the Wiener index.
-
Szeged index: The Szeged index extends the Wiener index for cyclic graphs by counting the number of atoms on both sides of each bond (those atoms only which are nearer to the given side of the bond than to the other), and sum these counts.
-
Wiener index: the average topological atom distance (half of the sum of all atom distances) in the molecule.
-
Wiener polarity: the number of 3 bond length distances in the molecule.
Other topological descriptors
-
Cyclomatic number: the smallest number of bonds which must be removed so that no circuit remains. Also known as circuit rank.
-
Fragment count: number of fragments in the sketch.
-
Steric effect index: topological steric effect index (TSEI) of an atom calculated from the covalent radii values and topological distances. The stericEffectIndex is related to the steric hindrance of the given atom.
-
Fsp3: number of sp3 hybridized carbons divided by the total carbon count.