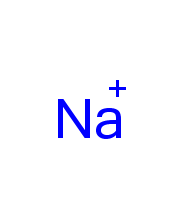Neutralize
The action neutralizes charged molecules. Neutralization logic is described below through examples.
Example :
|
Action |
Input |
Output |
Comment |
|
Neutralize |
|
|
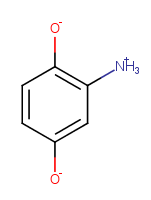
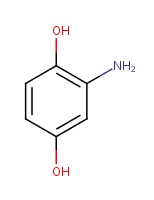
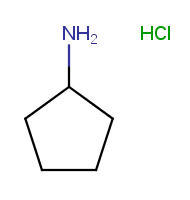
Charges of non-metal atoms are set to zero and implicit hydrogens are added/removed to neutralize the molecule. |
|
|
|
|
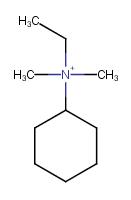
Metal ions are not neutralized. |
|
|
|
|
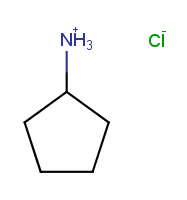
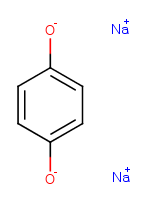
Charged structures with counterions are neutralized if each individual entity can be neutralized separately. |
|
|
|
|
Charged structures with counterions are not neutralized if the total charge of the structure is zero, and the structure contains individual entities which cannot be neutralized separately. |
|
|
|
|
If the molecule cannot be neutralized by charge manipulation and hydrogen addition/removal without violating valence rules, it remains unchanged. |
|
|
|
|
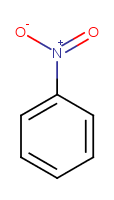
Mesomer structures with adjacent opposite charges remain intact. |
Note :
The action only operates through hydrogen manipulation, i.e. adds or removes hydrogens to create a neutral compound.