Markush DARC format (VMN)
VMN import is not supported since version 14.7.7.0.
Import from VMN format
Markush structure files complying the Markush DARC format are processed by Marvin, though with some limitations. The AMN file is looked for in the directory of the VMN file, with the same name and .amn extension (e.g. the AMN file of 46mrk001.vmn is 46mrk001.amn). The atom attributes and the AMN text notes are stored in atom properties, as described below.
Codename: vmn
Extension: .vmn
Interpretation of VMN features
-
Groups: G0 is read in as root structure while G1, G2, ... are stored in corresponding R-groups R1, R2, ... The representation of attachments is described below. -
Undefined attachment information is stored in form of position variation (variable attachment) bonds. -
Moieties are represented as repeating units with repetition ranges with no crossing bonds, but ignored (ungrouped) during search and enumeration. -
Multipliers are represented asrepeating units with repetition ranges with a single crossing bond, but ignored (ungrouped) during search and enumeration. -
Repeating units other than moieties and multipliers are described using a numerotation (numbering) attribute of three digits (e.g. 100) on the atoms of the repeating unit, with the appropriate repetition range text recorded in the corresponding AMN file (e.g. M100=1-4). Note, that there is a limitation on the number of elements in a repetition range (at most 10) and on the number of crossing bonds that can be processed (2 or 4). -
Structure shortcuts are read in as specific built-in abbreviated groups (superatom S-groups). -
Amino acids are read in by peptide import, which uses built-in abbreviated groups (superatom S-groups) to represent peptides. -
Superatoms are read in as pseudo-atoms and treated as homology groups. -
Atom attributes: we interpret the following VMN atom attributes:-
AM - Abnormal mass is stored in the mass number of the atom -
AV - Abnormal valence is stored in AV atom property -
DL - Peptide attribute is interpreted by peptide import
-
-
Homology atom attributes: we store the following VMN homology atom attributes in Marvin atom properties:VMN attribute nameMarvin atom property nameproperty valuesDT - Deuterium-Tritium countsDTCOUNTD[deuterium count]T[tritium count] (e.g. D3T2)CR - Carbon ring attributesBRANCHINGBRA, STRSIZELO, MID, HI, LO MID, MID HI, LO HISATURATIONSAT, UNSRINGTYPEMON, FUdata in AMNTEXTNOTESAMN text referring to the atom (e.g. N0-4,S0-4)For the interpretation of these attributes, refer to the Homology groups and Markush structures manual.
Structure shortcuts (abbreviated groups)
The following structure shortcuts (abbreviated groups) are supported:
|
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Amino acids (peptides)
The following standard amino acids (peptide abbreviated groups) are supported:
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
The following non-standard peptides are also supported:
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Note, that peptide connection bonds are not handled currently, therefore peptide sequences may not be correct.
For more information on peptide representation refer to the Sequences (peptide, DNA, RNA) documentation.
Superatoms (homology pseudo atoms)
Superatoms representing homology groups are read in as pseudo atoms. The following homologies are interpreted by enumeration and search:
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
For a detailed description of the interpretation, refer to the Homology groups and Markush structures manual.
Multiple R-group attachments
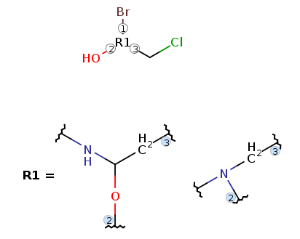
VMN format corrections
-
C0 is interpreted as CHK. -
C1 is interpreted as C. -
Deuterium/Tritium: we remove D and T ligands of the R-atoms. -
Homology groups being in rings are transformed to XX. -
R-group attachment bond type is transformed to parent R-atom bond type if different.
Limitations
Repeating units with repetition ranges
The number of elements in a repetition range is limited to 10 (e.g. range M100=2,5- is interpreted as M100=2,5-13). Repeating units with more than 4 crossing bonds are not processed by search and enumeration.
Superatoms (homologies) that are not supported
The following superatoms (homologies) are not supported by search and enumeration (but read in and displayed as pseudo-atoms):
|
|
|
|
|
The detailed description of homology interpretation is described in the Homology groups and Markush structures manual.
Atom attributes that are not processed by search and enumeration
The following atom attributes are not processed by search and enumeration (but displayed in atom labels):
|
|
|
|
|
|
Export to VMN format
VMN export is not available yet.
References
-
The Markush DARC Format, T Ferns, Internal Technical Report, Thomson Scientific, 2002 -
Derwent World Patents Index, Markush DARC User Manual, The Thomson Corporation, 1993, 2008