.ChemAxon Synergy integration workshop vLatest
Table of Contents
1. Prerequisites
-
Your favourite Java IDE
-
Spring Boot CLI: https://docs.spring.io/spring-boot/docs/current/reference/html/getting-started-installing-spring-boot.html#getting-started-installing-the-cli
-
Git client
-
Heroku account: https://signup.heroku.com/
-
Heroku CLI: https://devcenter.heroku.com/articles/heroku-cli
-
CXN Pass account: https://pass.chemaxon.com/
-
Synergy demo instance: https://team1.synergy-dev.cxcloud.io
Optionally check these to verify settings:
java -versionjava version "1.8.x"Java(TM) SE Runtime Environment (build 1.8.x)Java HotSpot(TM) 64-Bit Server VM ...spring --versionSpring CLI v1.5.3.RELEASEgit --versiongit version 2.9.0.heroku --versionheroku-cli/5.9.1-3d5ebd1 ... go1.7.52. Generate a Spring Boot app
2.1 Create a Spring Boot application
spring init --package-name=com.example --dependencies=web,actuator --boot-version=1.5.6.RELEASE example-synergy-appcd example-synergy-app./mvnw spring-boot:run2.2 Try to open health check page
3. Add a simple endpoint
3.1 Open the generated Maven project in your favourite IDE.
3.2 Create a welcome service
Add this class to package com.example:
package com.example;import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ResponseBody;@Controllerpublic class HomeController { @RequestMapping("/") @ResponseBody Object home() { return "Hello Synergy!"; }}3.3 Run/restart the application
./mvnw spring-boot:run3.4 Check welcome service in a browser
4. App info endpoint
Our application’s app-info endpoint should look like this:
{ "displayName": "Example Synergy app", "address": "http://localhost:8080/", "identities": [ { "category": "service", "type": "computation" }, { "category": "application", "type": "service" } ], "features": [ { "namespace": "synergy/health", "attributes": { "url": "http://localhost:8080/health" } }, { "namespace": "synergy/icon", "attributes": { "url": "https://www.gravatar.com/avatar/457372368cbaf7fce1427ce46fc4b199?s=64&d=identicon" } }, { "namespace": "producer-service", "attributes": { "url": "http://localhost:8080/produce" } } ]}We are defining here a service called producer-service, that is a sample for a custom service provided by your application, we will implement it later.
4.1 Create class AppInfoController
package com.example;import java.security.MessageDigest;import java.util.Arrays;import java.util.LinkedHashMap;import java.util.Map;import java.util.Optional;import java.util.function.Supplier;import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;import javax.xml.bind.DatatypeConverter;import org.slf4j.Logger;import org.slf4j.LoggerFactory;import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ResponseBody;import org.springframework.web.servlet.support.ServletUriComponentsBuilder;import org.springframework.web.util.UriComponentsBuilder;@Controllerpublic class AppInfoController { private static final Logger LOG = LoggerFactory.getLogger(AppInfoController.class); @Value("${producer.name:#{null}}") private String producerName; @RequestMapping("/app-info") @ResponseBody Object appInfo(final HttpServletRequest request) throws Exception { Supplier<UriComponentsBuilder> uriBuilder = () -> ServletUriComponentsBuilder.fromContextPath(request) ; // TODO: give the application some nice name String applicationDisplayName = "Example Synergy app"; Map<String, Object> info = new LinkedHashMap<>(); info.put("displayName", applicationDisplayName); String address = uriBuilder.get().replacePath("/").toUriString(); info.put("address", address); info.put("identities", Arrays.asList( identity("service", "computation"), identity("application", "service"))); // generate a unique hash for the application String hash = DatatypeConverter.printHexBinary( MessageDigest.getInstance("md5").digest(address.getBytes())).toLowerCase(); // TODO: give the producer service some custom unique name String producerServiceName = Optional.ofNullable(producerName).orElse(hash + "-producer"); info.put("features", Arrays.asList( feature("synergy/health", uriBuilder.get().replacePath("/health").toUriString()), feature("synergy/icon", String.format("https://www.gravatar.com/avatar/%s?s=64&d=identicon", hash)), feature(producerServiceName, uriBuilder.get().replacePath("/produce").toUriString()))); return info; } /** Helper methods for assembling app-info json **/ private static Map<String, Object> identity(final String category, final String type) { Map<String, Object> identity = new LinkedHashMap<>(); identity.put("category", category); identity.put("type", type); return identity; } private static Map<String, Object> feature(final String namespace, final String url) { Map<String, Object> feature = new LinkedHashMap<>(); feature.put("namespace", namespace); Map<String, Object> attributes = new LinkedHashMap<>(); attributes.put("url", url); feature.put("attributes", attributes); return feature; }}4.2 Run/restart the application
./mvnw spring-boot:run4.3 Check application info in a browser
5. Deploy to Heroku
5.1 Create a Git repo and commit your sources
git initgit add .git commit -m "first commit"5.2 Create Heroku app and deploy the application
heroku loginheroku creategit push heroku masterheroku open6. Register app into Synergy
If you send us your deployment’s application info URL, we’ll register it for you!
7. Implement authentication
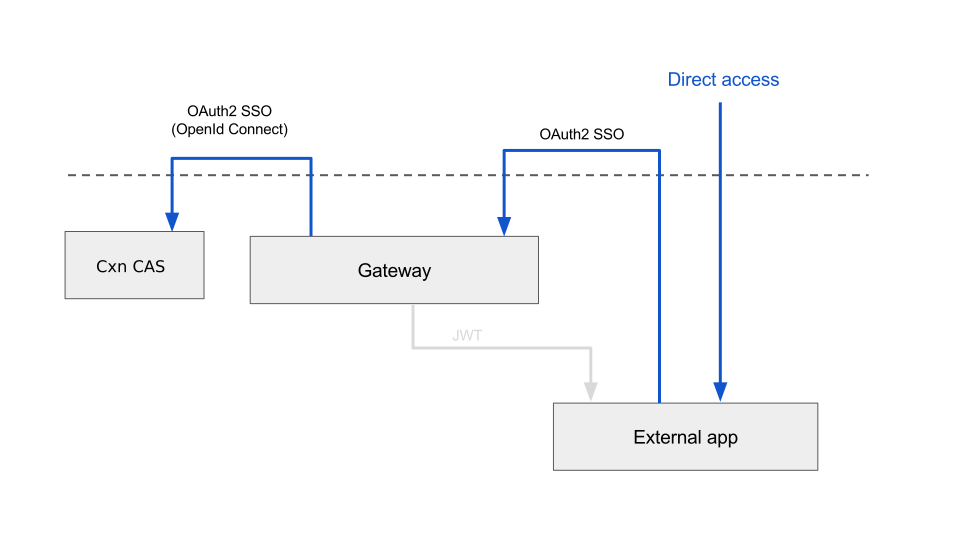
7.1 Add security dependencies
Add new dependencies in your pom.xml:
<dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-security</artifactId></dependency><dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.security.oauth</groupId> <artifactId>spring-security-oauth2</artifactId></dependency><dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.security</groupId> <artifactId>spring-security-jwt</artifactId></dependency>7.2 Enable Oauth2 SSO for Spring Boot app
It can be done by adding @EnableOAuth2Sso annotation.
Security must be disabled on health and app-info endpoints.
Create class SynergySecurityConfiguration, extend WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter and override configure method:
package com.example;import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.security.oauth2.client.EnableOAuth2Sso;import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;import org.springframework.security.config.annotation.web.builders.WebSecurity;import org.springframework.security.config.annotation.web.configuration.WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter;@Configuration@EnableOAuth2Ssopublic class SynergySecurityConfiguration extends WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter { @Override public void configure(final WebSecurity web) throws Exception { web.ignoring().antMatchers( "/app-info", "/health"); }}7.3 Set configuration required by OAuth2
Rename empty config file application.properties to application.yml.
Add these to application.yml:
security: oauth2: client: clientId: [your app's client id] clientSecret: [your app's client secret] accessTokenUri: https://team1.synergy-dev.cxcloud.io/oauth/token userAuthorizationUri: https://team1.synergy-dev.cxcloud.io/oauth/authorize resource: jwt.key-uri: https://team1.synergy-dev.cxcloud.io/public/publickey/ssh-rsa.jsonAsk for your client id and client secret!
7.4 Commit & Deploy
git add .git commit -m "configure authentication"git push heroku master7.5 Open your app directly on Heroku
heroku openThere should be a redirect to authenticate you when opening the application. (You my not nitice it, when already logged in to Synergy.)
8. Print user info
8.1 Extract custom token data
Create class SynergyAccessTokenConfigurer and implement JwtAccessTokenConverterConfigurer:
package com.example;import java.util.Collection;import java.util.Collections;import java.util.Map;import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.security.oauth2.resource.JwtAccessTokenConverterConfigurer;import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;import org.springframework.security.authentication.UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken;import org.springframework.security.core.Authentication;import org.springframework.security.core.GrantedAuthority;import org.springframework.security.oauth2.provider.token.DefaultAccessTokenConverter;import org.springframework.security.oauth2.provider.token.DefaultUserAuthenticationConverter;import org.springframework.security.oauth2.provider.token.UserAuthenticationConverter;import org.springframework.security.oauth2.provider.token.store.JwtAccessTokenConverter;@Configurationpublic class SynergyAccessTokenConfigurer implements JwtAccessTokenConverterConfigurer { @Bean UserAuthenticationConverter userAuthenticationConverter() { return new DefaultUserAuthenticationConverter() { @Override public Authentication extractAuthentication(final Map<String, ?> token) { Collection<? extends GrantedAuthority> authorities = Collections.emptyList(); // Use whole token as user principal return new UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken(token, "N/A", authorities); } }; } @Override public void configure(final JwtAccessTokenConverter converter) { DefaultAccessTokenConverter accessTokenConverter = new DefaultAccessTokenConverter(); accessTokenConverter.setUserTokenConverter(userAuthenticationConverter()); converter.setAccessTokenConverter(accessTokenConverter); }}8.2 Return token data in welcome service
Return the user principal in the welcome service, modify HomeController:
package com.example;import java.util.LinkedHashMap;import java.util.Map;import org.springframework.security.core.context.SecurityContextHolder;import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ResponseBody;@Controllerpublic class HomeController { @RequestMapping("/") @ResponseBody Object home() { Map<String, Object> result = new LinkedHashMap<>(); // return user principal as a json element result.put("user", SecurityContextHolder.getContext().getAuthentication().getPrincipal()); return result; }}
Modified lines are highlighted.
8.3 Commit & Deploy
git add .git commit -m "print userinfo"git push heroku masterYou should see the Synergy token in json format. (Contains information about the user who is logged in.)
9. Implement authentication of rest endpoints
Public rest enpoints must understand Synergy tokens sent in a http header.
9.1 Create resource server configuration
Create new class ResourceServerConfiguration:
package com.example;import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;import org.springframework.security.config.annotation.web.builders.HttpSecurity;import org.springframework.security.oauth2.config.annotation.web.configuration.EnableResourceServer;import org.springframework.security.oauth2.config.annotation.web.configuration.ResourceServerConfigurerAdapter;import org.springframework.security.oauth2.config.annotation.web.configurers.ResourceServerSecurityConfigurer;import org.springframework.security.web.util.matcher.RequestHeaderRequestMatcher;import org.springframework.security.web.util.matcher.RequestMatcher;@Configuration@EnableResourceServerpublic class ResourceServerConfiguration extends ResourceServerConfigurerAdapter { @Bean("resourceServerRequestMatcher") public RequestMatcher resources() { return new RequestHeaderRequestMatcher("Authorization"); } @Override public void configure(final HttpSecurity http) throws Exception { http .requestMatcher(resources()).authorizeRequests() .anyRequest().authenticated(); } @Override public void configure(final ResourceServerSecurityConfigurer resources) throws Exception { // we acccept tokens for any resourceId resources.resourceId(null); }}Notice here we have created a RequestMatcher to separate API calls. For now it is matched when request contains an Authorization header (which should contain the token).
9.2 Modify SynergySecurityConfiguration
package com.example;import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Qualifier;import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.security.oauth2.client.EnableOAuth2Sso;import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;import org.springframework.security.config.annotation.web.builders.HttpSecurity;import org.springframework.security.config.annotation.web.builders.WebSecurity;import org.springframework.security.config.annotation.web.configuration.WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter;import org.springframework.security.web.util.matcher.NegatedRequestMatcher;import org.springframework.security.web.util.matcher.RequestMatcher;@Configuration@EnableOAuth2Ssopublic class SynergySecurityConfiguration extends WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter { @Autowired @Qualifier("resourceServerRequestMatcher") private RequestMatcher resources; @Override protected void configure(final HttpSecurity http) throws Exception { RequestMatcher nonResoures = new NegatedRequestMatcher(resources); http .requestMatcher(nonResoures).authorizeRequests() .anyRequest().authenticated(); } @Override public void configure(final WebSecurity web) throws Exception { web.ignoring() .antMatchers( "/app-info", "/health"); }}Now SSO is only configured for requests which does not handled by resource server configuration.
10. Demonstrate application to application communication
10.1 Create ServiceController and implement a producer service
package com.example;import java.util.LinkedHashMap;import java.util.Map;import java.util.Random;import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;import org.slf4j.Logger;import org.slf4j.LoggerFactory;import org.springframework.security.core.context.SecurityContextHolder;import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ResponseBody;@Controllerpublic class ServiceController { private static final Logger LOG = LoggerFactory.getLogger(ServiceController.class); @RequestMapping("/produce") @ResponseBody Object produce(final HttpServletRequest request) throws Exception { LOG.info("produce called by: {}", SecurityContextHolder.getContext().getAuthentication()); Map<String, Object> result = new LinkedHashMap<>(); // TODO: add your custom data or computation to the result result.put("data", new Random().nextInt()); result.put("producedBy", request.getRequestURL()); return result; }}10.2 Create helper class for obtaining token for your application
package com.example;import java.util.Arrays;import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;import org.springframework.security.oauth2.client.resource.OAuth2ProtectedResourceDetails;import org.springframework.security.oauth2.client.token.DefaultAccessTokenRequest;import org.springframework.security.oauth2.client.token.grant.client.ClientCredentialsAccessTokenProvider;import org.springframework.security.oauth2.client.token.grant.client.ClientCredentialsResourceDetails;import org.springframework.security.oauth2.common.OAuth2AccessToken;import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;@Componentpublic class ClientCredentialsTokenProvider { private final ClientCredentialsAccessTokenProvider tokenProvider = new ClientCredentialsAccessTokenProvider(); private final String accessTokenUri; private final String clientId; private final String clientSecret; @Autowired public ClientCredentialsTokenProvider(final OAuth2ProtectedResourceDetails resourceDetails) { this( resourceDetails.getAccessTokenUri(), resourceDetails.getClientId(), resourceDetails.getClientSecret()); } public ClientCredentialsTokenProvider( final String accessTokenUri, final String clientId, final String clientSecret) { this.accessTokenUri = accessTokenUri; this.clientId = clientId; this.clientSecret = clientSecret; } public OAuth2AccessToken getToken(final String... scopes) { ClientCredentialsResourceDetails resourceDetails = new ClientCredentialsResourceDetails(); resourceDetails.setAccessTokenUri(accessTokenUri); resourceDetails.setClientId(clientId); resourceDetails.setClientSecret(clientSecret); resourceDetails.setScope(Arrays.asList(scopes)); return tokenProvider.obtainAccessToken(resourceDetails, new DefaultAccessTokenRequest()); }}10.3 Create RestTemplateConfiguration
It configures a rest service client to forward the current OAuth2 token in Authorization header of each request.
package com.example;import java.util.Optional;import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;import org.springframework.security.core.context.SecurityContextHolder;import org.springframework.security.oauth2.provider.OAuth2Authentication;import org.springframework.security.oauth2.provider.authentication.OAuth2AuthenticationDetails;import org.springframework.web.client.RestTemplate;@Configurationpublic class RestTemplateConfiguration { @Autowired private ClientCredentialsTokenProvider tokenProvider; @Bean public RestTemplate restTemplate() { RestTemplate template = new RestTemplate(); template.getInterceptors().add((request, body, execution) -> { final String token; Optional<OAuth2AuthenticationDetails> currentOAuth2Details = currentOAuth2Details(); if (currentOAuth2Details.isPresent()) { // get token from current security context token = currentOAuth2Details.get().getTokenValue(); } else { // request a new token as an application (server-to-server communication) token = tokenProvider.getToken("read").getValue(); } // forward token in Authorization header request.getHeaders().add("Authorization", "Bearer " + token); return execution.execute(request, body); }); return template; } private static Optional<OAuth2AuthenticationDetails> currentOAuth2Details() { return Optional.ofNullable(SecurityContextHolder.getContext().getAuthentication()) .filter(OAuth2Authentication.class::isInstance) .map(OAuth2Authentication.class::cast) .map(OAuth2Authentication::getDetails) .map(OAuth2AuthenticationDetails.class::cast); }}10.4 Create DiscoveryClient
It’s a client for Synergy service discovery.
package com.example;import java.util.LinkedHashMap;import java.util.Map;import java.util.Optional;import java.util.stream.StreamSupport;import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;import org.springframework.web.client.RestTemplate;import com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.JsonNode;@Componentpublic class DiscoveryClient { @Autowired private RestTemplate restTemplate; @Value("${synergy.url}/api/discover") private String discoveryUrl; public String getFeatureUrl(final String namespace) { Map<String, String> all = findFeature(namespace); if (all.isEmpty()) { throw new IllegalArgumentException("No applications found with feature " + namespace); } if (all.size() > 1) { throw new IllegalArgumentException("Mutiple applications found with feature " + namespace + ": " + all.keySet()); } return all.entrySet().iterator().next().getValue(); } private Map<String, String> findFeature(final String namespace) { Map<String, String> result = new LinkedHashMap<>(); for (JsonNode application : restTemplate.getForObject(discoveryUrl, JsonNode.class)) { Optional<String> featureUrl = StreamSupport.stream(application.get("features").spliterator(), false) .filter(feature -> feature.get("namespace").asText().equals(namespace)) .map(feature -> feature.get("attributes").get("url").asText()) .findFirst(); if (featureUrl.isPresent()) { result.put(application.get("displayName").asText(), featureUrl.get()); } } return result; }}10.5 Create App2AppCommunication
It contains an 2 endpoint for consuming another application’s producer service:
-
one using the token of the logged in user /consume
-
one is requesting a new token in the name of your application (server-to-server communication) /consume-as-app
package com.example;import java.util.LinkedHashMap;import java.util.Map;import java.util.concurrent.FutureTask;import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;import org.slf4j.Logger;import org.slf4j.LoggerFactory;import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;import org.springframework.security.core.context.SecurityContextHolder;import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PathVariable;import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;import org.springframework.web.client.RestTemplate;import com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.JsonNode;@RestControllerpublic class App2AppCommunication { private static final Logger LOG = LoggerFactory.getLogger(App2AppCommunication.class); @Autowired private RestTemplate template; @Autowired private DiscoveryClient discovery; @RequestMapping("/consume/{namespace}") public Object consumeAsUser(@PathVariable("namespace") final String namespace, final HttpServletRequest request) throws Exception { LOG.info("consumeAsUser called by: {}", SecurityContextHolder.getContext().getAuthentication().getPrincipal()); return consume(namespace, request); } @RequestMapping("/consume-as-app/{namespace}") public Object consumeAsApp(@PathVariable("namespace") final String namespace, final HttpServletRequest request) throws Exception { LOG.info("consumeAsApp called by: {}", SecurityContextHolder.getContext().getAuthentication().getPrincipal()); // call consume on other thread (without security context) FutureTask<Object> task = new FutureTask<>(() -> consume(namespace, request)); new Thread(task).start(); return task.get(); } private Object consume(final String namespace, final HttpServletRequest request) throws Exception { // discover remote service String remoteServiceUrl = discovery.getFeatureUrl(namespace); // call remote service JsonNode producerResult = template.getForObject(remoteServiceUrl, JsonNode.class); Map<String, Object> result = new LinkedHashMap<>(); result.put("producerResult", producerResult); result.put("consumedBy", request.getRequestURL()); return result; }}10.6 Configure discovery service
heroku config:set synergy.url=https://team1.synergy-dev.cxcloud.io10.7 Commit & Deploy
git add .git commit -m "app2app communication"git push heroku master10.8 Open your app directly on Heroku, ask for name of another service (or use yours)
heroku open /consume/{name-of-another-service}
heroku open /consume-as-app/{name-of-another-service}10.9 Display application logs to check communication
heroku logs -t