Red and blue representation of pKa values
This manual explains the difference between the representations of coloured pKa values:
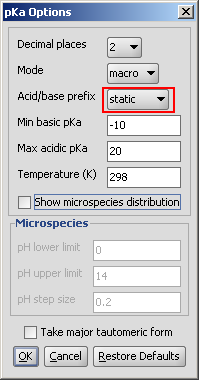
Static red & blue representation of pK a values
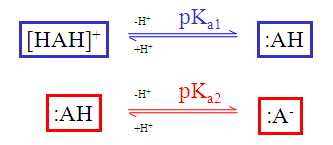
The static (default) red & blue colour annotation is related to the ionization steps shown in the figure below.
|
|
Fig. 1 Static red & blue colouring schema
The
static red & blue coloring schema
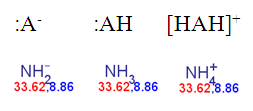
does not depend on the ionic form of a molecule submitted to the pKa calculation. The next three species have the same pKa values and the same colour.
|
|
Fig. 2 Calculated pKa of the deprotonated, neutral and the protonated forms of ammonia in the static red & blue colouring schema
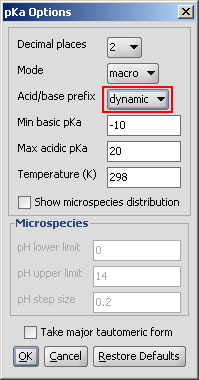
Dynamic red & blue representation of pK a values
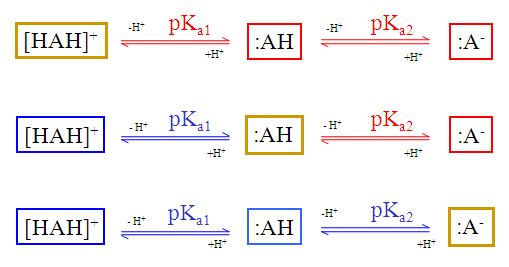
The dynamic (non-default setting) red & blue colouring schema depends on the submitted molecule.
|
|
Fig. 3 Dynamic red & blue colouring schema
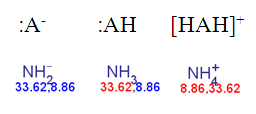
The result of the previous ammonia example with the non-default pKa calculation:
|
|
Fig. 4 Calculated pKa of deprotonated, neutral, and the protonated forms of ammonia according to the dynamic red & blue colouring schema
Differences between the static and the dynamic red & blue colouring schema are summarized in the following table.
|
|
static |
dynamic |
|
Subject of calculation |
neutral state of the submitted molecule |
the submitted molecule |
|
Blue color assigned to |
the acid dissociation constant between the neutral base and its conjugated acid |
the acid dissociation constant between the submitted base and its conjugated acid |
|
Red color assigned to |
the acid dissociation constant between the neutral acid and its conjugated base |
the acid dissociation constant between the submitted acid and its conjugated base |
|
setting in the Options panel |
|
|
Tab. 1 Differences between the static and dynamic red & blue colouring schema