Molecular Surface Area Plugin 3D
This manual gives you a walk-through on how to use the Molecular Surface Area (3D) Plugin:
Introduction
There are two types of available molecular surface area calculations, van der Waals (vdW) and solvent accessible (SA). The calculation method is based on Ferrara et al.
The result window contains the area and the molecule in 3D view. The left window shows the vdW surface, while the right one the SASA.
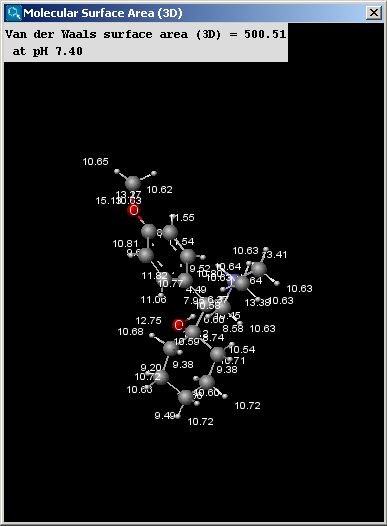
Fig. 1 Van der Waals surface area calculation results
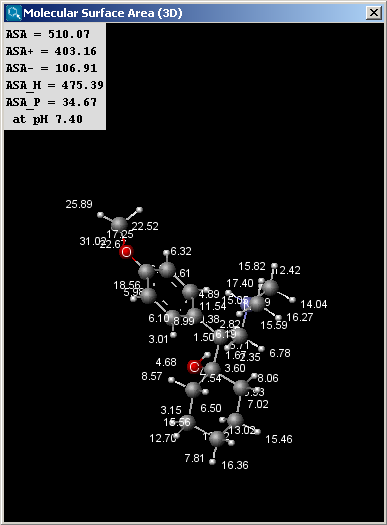
Fig. 2 Solvent-accessible surface area calculation results
Options
The calculation and the display options can be set in the Molecular Surface Area (3D) Options panel:
-
Decimal places: sets the number of decimal places for the result values.
-
Surface Area
-
Van der Waals: calculates the van der Waals surface of the molecule (in Å2).
-
Solvent Accessible: calculates the solvent accessible surface of the molecule (in Å2).
-
-
Solvent radius: sets the radius of the solvent molecule (by default water, 1.4 Å).
-
Show surface area increments: if set, atomic increments are shown.
-
Take major microspecies at pH: the surface area of the major microspecies present at the given pH is calculated.
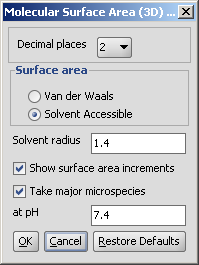
Fig. 3 Options panel
The values indicated in the text field of solvent accessible surface area calculation are the following (all in Å2):
-
ASA: solvent accessible surface area calculated using the radius of the solvent (1.4 Å for the water molecule)
-
ASA+: solvent accessible surface area of all atoms with positive partial charge (strictly greater than 0)
-
ASA-: solvent accessible surface area of all atoms with negative partial charge (strictly less than 0)
-
ASA_H: solvent accessible surface area of all hydrophobic (|qi|<0.125) atoms (|qi| is the absolute value of the partial charge of the atom)
-
ASA_P: solvent accessible surface area of all polar (|qi|>0.125) atoms (|qi| is the absolute value of the partial charge of the atom)