HTTP
This manual will give you a walk-through on how to use the HTTP web services.
Introduction
HTTP Service is the most lightweight and unrestricted remote service: it supports POST and GET requests to a predefined URL. Result is retrieved as is and rendered as a webpage.
Examples
Example #1
This example will show how to call chemicalize.org via an HTTP web service. In this case we want to calculate the pKa values of a molecule.
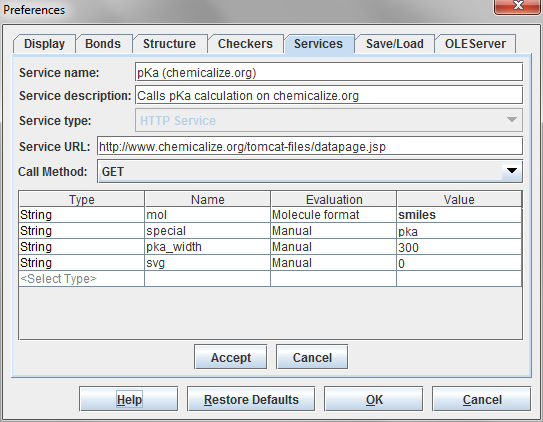
Fig. 1 HTTP service calling the pKa calculator of chemicalize.org
An example calculation with this webservice can be found below.
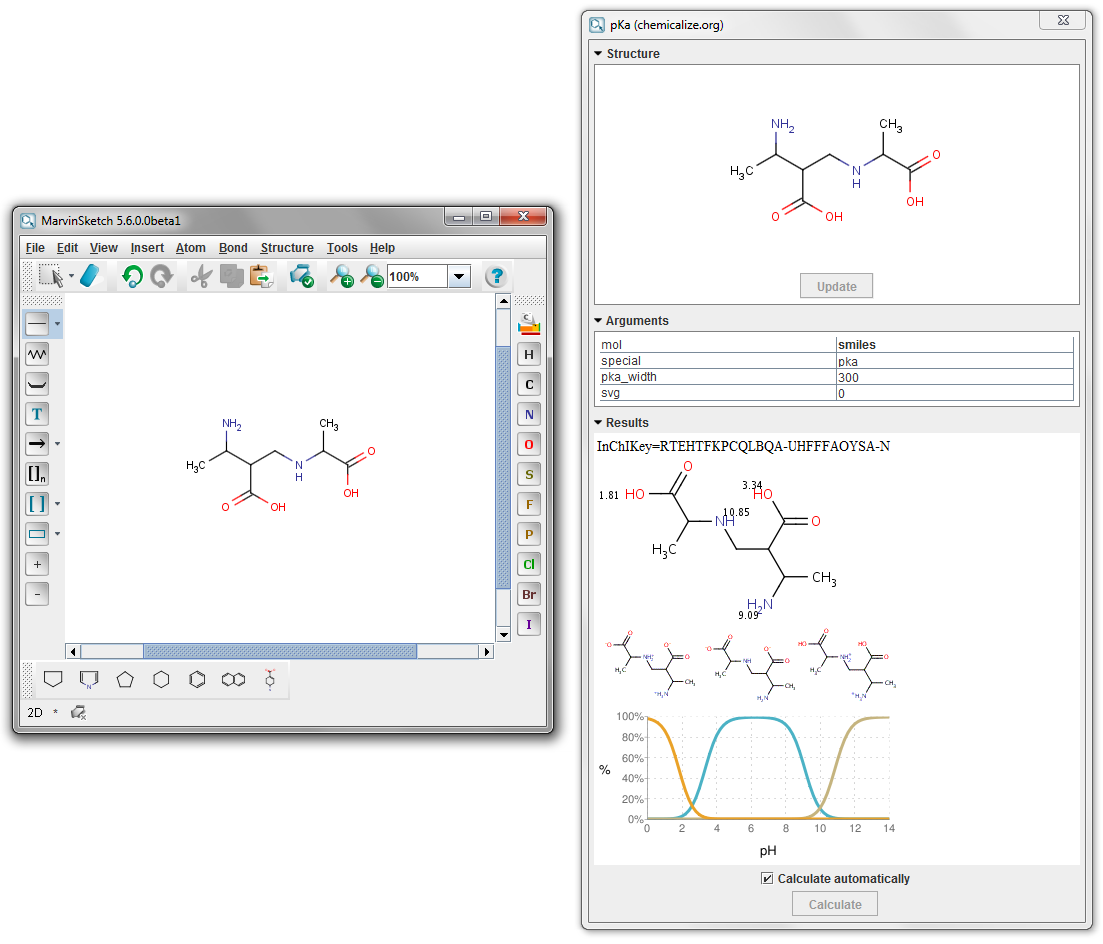
Fig. 2 Result of the pKa calculation via the webservice calling chemicalize.org
Example #2
This example shows how to reach the functionalities of chemicalize.org via HTTP API.
HTTPServiceDescriptor descriptor = new HTTPServiceDescriptor(); descriptor.setURL("http://chemicalize.org/tomcat-files/datapage.jsp"); descriptor.addArgument(ServiceArgument.createArgument("mol", "")); descriptor.addArgument(ServiceArgument.createArgument("special", "")); descriptor.addArgument(ServiceArgument.createArgument("pka_width", 0)); Object result = null; try { result = descriptor.getServiceHandler().callService(descriptor, "c1ccnccc1", "pka", 300); } catch (ServiceException e) { System.err.println("Service call failed."); } System.out.println("Synchronized call returned: " + String.valueOf(result)); descriptor.getServiceHandler().callService(descriptor, new AsyncCallback<String>() { @Override public void onSuccess(String result) { System.out.println("Aynchronous call returned: " + result); } @Override public void onFailure(ServiceException caught) { System.err.println("Asynchronous call failed."); } }, "c1ccnccc1", "pka", 300);